Beam-splitter
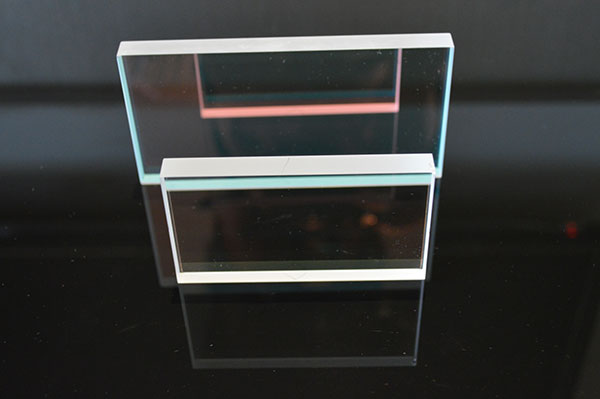
Beamsplitters are used to split or combine beams of light. Plates are used for most laser applications as they exhibit low absorption. Cubes are a convenient, protected form for low power applications. The performance of a beamsplitter is mainly dependent on the coating specifications.
|
Beamsplitter
|
Spectrum
|
Properties
|
|
Beamsplitter plate
|
Broadband Wavelength
|
Beamsplitter plates can be used with high power lasers. When using beamsplitter plates, it is important to bear in mind that the two partial beams travel different optical paths. The optical paths depend on the incident angle and the thickness of the plates.
|
|
Single Wavelength
|
||
|
Beamsplitter Cube
|
Broadband Wavelength
|
Compare with beamsplitter plates, beamsplitter cubes have the following advantages:
-Identical path lengths for both the reflected and the transmitted beams -The transmitted beam is neither display nor deflected -Stable and compact -Easy operation -Easy to mount / align |
|
Single Wavelength
|
||
|
Polarizering Beamsplitter cube
|
Broadband Wavelength
|
The prism can be used as polarizers, beamsplitters, or beam combiners. The output beam, which is parallel to the input beam, is called a p-polarized beam while the orthoganal output beam is defined as the s-polarized beam.
|
|
Single Wavelength
|
Beamsplitter Plates Capability
|
Attribute
|
Commercial
|
High precision
|
|
Material
|
BK7
|
BK7
|
|
Dimension Tolerance
|
±0.1mm
|
±0.02mm
|
|
Thickness Tolerance
|
±0.1mm
|
±0.02mm
|
|
Flatness
|
Per 25.4mm λ/4 @ 632.8nm
|
Per 25.4mm λ/10 @ 632.8nm
|
|
Surface Quality
|
60-40 scratch and dig
|
10-5 scratch and dig
|
|
Parallelism
|
<20 arc seconds
|
<5 arc seconds
|
|
T/R
|
T=(Ts+Tp)/2,R=(Rs+Rp)/2
T/R=50/50, 80/20, 70/30, 90/10, 60/40 ±5% @ λ c or λ b |
T=(Ts+Tp)/2,R=(Rs+Rp)/2
T/R=50/50, 80/20, 70/30, 90/10, 60/40 ±3% @ λ c or λ b |
|
Coating
|
λ c: Single wavelength, λ b: Broadband wavelength
|
|


